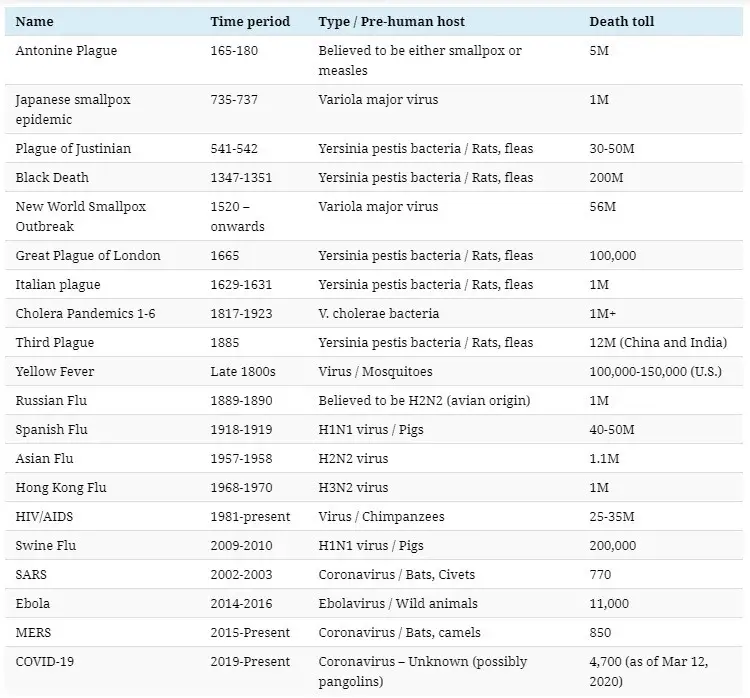
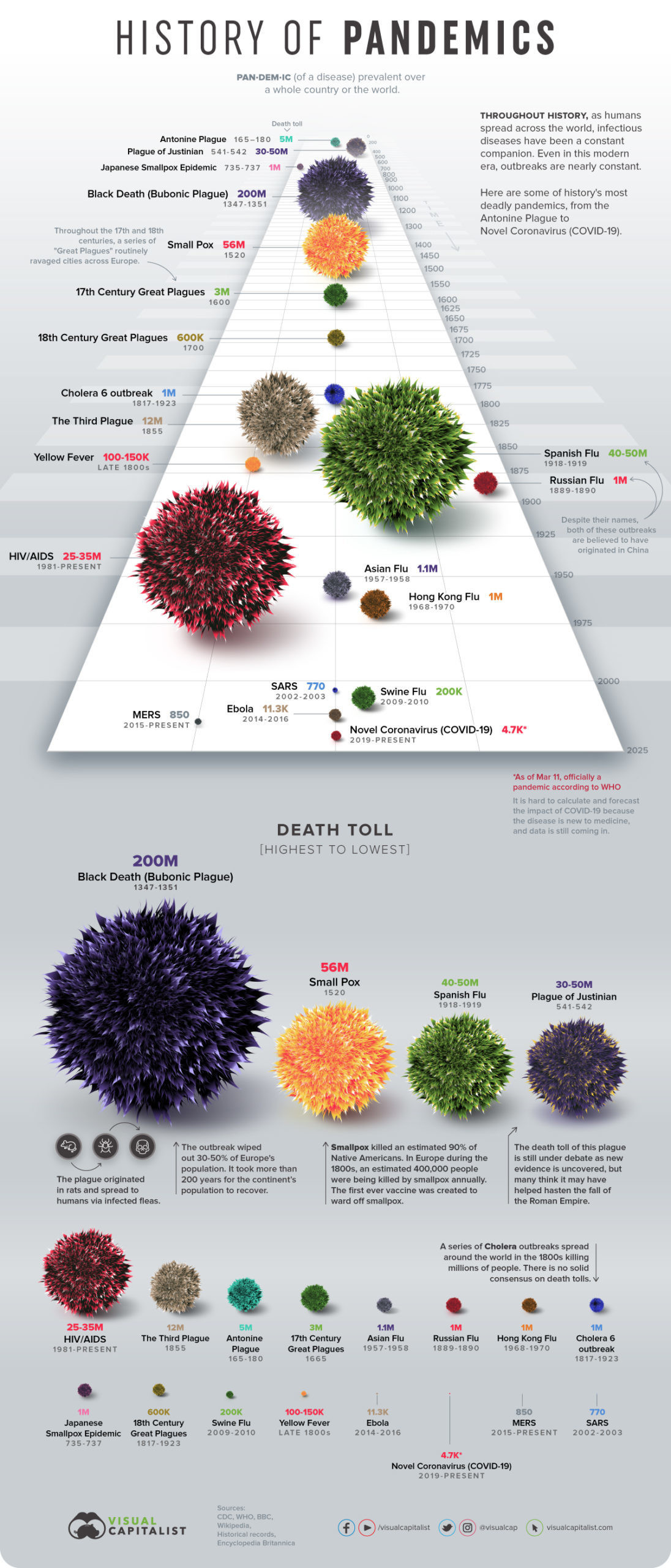
This Infographic Visualizes The History Of Pandemics By Death Toll
Tags: opinion

Recently, the World Health Organization (WHO) has declared the Coronavirus (COVID-19) outbreak a pandemic. A pandemic is any kind of disease that has spread over a large area of land and in this case, the entire world. It has been happening for centuries and the reason for it spreading so rapidly is the human settlements. Once the agrarian communities emerged and trade relations were established, diseases cropped up. Smallpox, leprosy, malaria, tuberculosis, and influenza showed up at an early stage. Pandemics are connected with the rise of human civilization.
The bigger cities, contact with various kinds of people, different animals, and different ecosystems meant that diseases would increase. The pandemics have appeared one after another but the dead rates have consistently decreased with time. There have been new medical discoveries and improvements in healthcare to dull the effect of pandemics.
Also Read: This Politician Is Striving To Make Coronavirus Testing Free In America, That’s A Challenge
Fury of the Gods
Ancient society was primarily a theological society where everything was explained in terms of God. If there was rain it’d be God’s blessing and if there was flood it’d be his fury. People believed that the supernatural powers of the Universe brought down diseases upon human beings because of their deeds. The lack of logical reasoning made the pandemics worse and millions of people lost their lives.
Image: Visual Capitalist
One of the earliest pandemics was Justinian’s plague. According to Procopius of Caesarea, the Byzantine historian, the great plague started from China or North-East India. It was through land and sea trade routes that the Yersinia pestis bacteria entered the Byzantine via the Mediterranean ports. Procopius had a great understanding of the vital part geography and trade relations played in the spread of the pandemic. However, he blamed Emperor Justinian for it was his actions that brought upon God’s fury. A possible explanation for this blame could be the emperor’s efforts to unite the Eastern and Western remnants of the Roman Empire. This period has been termed as the “Dark Ages” by historians. The evolution of people’s understanding of pandemics shows a leaning towards scientific explanations than superstitions.
Trading Diseases
Since most pandemics could be tracked down to trade relations, the practice of quarantine came to exist in the 14th century. This was done to stop the disease from spreading in the coastal cities and take the shape of a pandemic. In Venice, when the ships came from a diseased port, it had to sit at the anchor for more than a month before landing. During the 19th century, there was a cholera outbreak in London and people thought of quarantine as the only way out. It is crucial for all pandemics across time.
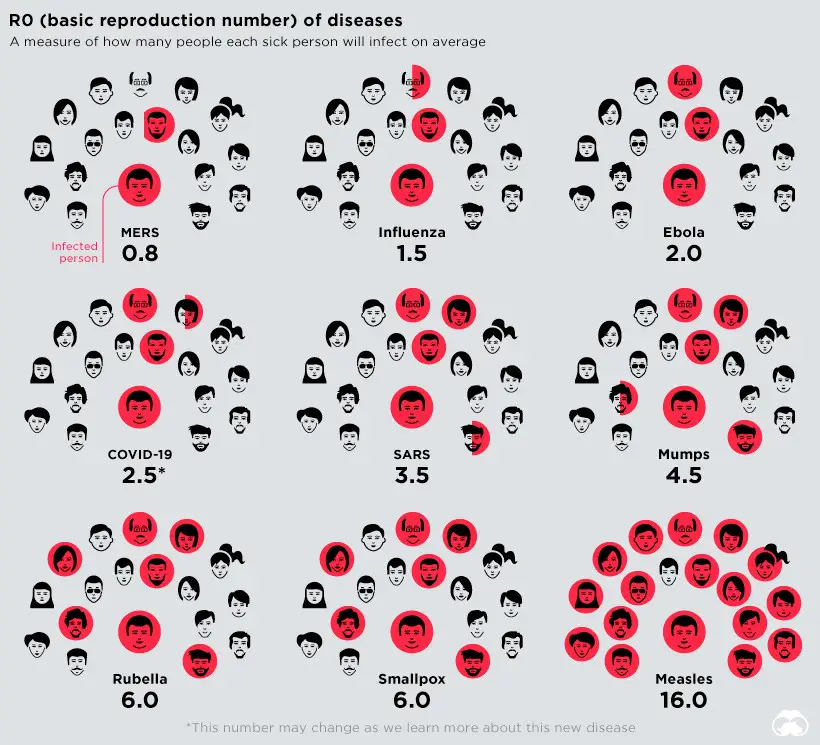
How Infectiousness Works
The R0 or “R naught” is used by scientists to determine the infectiousness of a disease. It indicates the number of people who have been affected and how many people can be susceptible to the disease on average. Measles tops the chart with an R0 range of 12-18. The R0 of the COVID-19 is yet to be determined.
Also Read: This Insightful 3D Medical Animation Explains The Coronavirus Epidemic
The Rise Of The Cities And Pandemics
The denser the neighborhood, the greater the chances of people being affected bt pandemics. The climate crisis also facilitates the spreading of diseases as it is already polluted. While the whole world is in self-quarantine, the digital network keeps everyone connected.
Pandemics can be controlled with conscious efforts, it is time to be in quarantine. Stay safe!
Leave Comment: